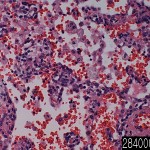
| Product name | Lung bronchopneumonia |
| Cat. No. | 2840000A |
| No. of samples | 1 |
| Description | lung, bronchopneumonia Age/Sex : 71/M |
| Price | 197 EUR |
| 260 USD | |
| 170 GBP |
Product Related Literature
It is an acute inflammation of the bronchial wall (please not to be confused with lobar pneumonia) bronchial pneumonia and bronchial pneumonia and bronchial pneumonia. This is a kind of pneumonia characterization effects on the lungs portion of one or more isolated, the foci of acute connecting a plurality. It is one of the two types of bacterial pneumonia classified Integration (coagulation), the total anatomical distribution of the large leaves pneumonia other.
Pneumonia, there is less likely lobar pneumococcus than are associated. In particular organism such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa Staphylococcus aureus such, Klebsiella, and Escherichia coli, I was bronchial pneumonia related to nosocomial pneumonia. Lead to inflammatory immune response, in bacterial pneumonia, and bacterial invasion from the lung parenchyma. This reaction leads to the filling of the alveolar sacs and exudate. Loss of exchange with the fluid and air space, is called consolidation. In pneumonia or lobular pneumonia, affect the lobes of one or more lesions of multiple, isolated acute consolidated. The leaflets and lung, these two types of pneumonia is the anatomical categories classical, but in bacterial pneumonia clinical species, that the model used as the overlap is generally difficult. In many cases, bronchopneumonia (lobular) leads to the progress of the rover pneumonia infection. The same body, the patient may lead to the type of pneumonia in patients with another. From the viewpoint of clinical very important, show an accurate assessment of the extent of the disease and its causes to distinguish anatomical subtype of pneumonia.
Multiple foci of consolidation are located in the base sheet both sides, often of human lung. These lesions, 2-4 cm in diameter, gray, yellow, dry, often, it is limited a little with a focus on the bronchioles, the children, tend to merge in particular. Focus of inflammation condensation, acute bronchiolitis will focus on the bronchioles using the (- purulent exudate in the lumen and parietal inflammation – pus). Alveolar lumen is filled with neutrophils (“white blood cell alveolitis”) in peribronchiolar. Massive congestion is present. Inflammatory lesions, separated by aeration real normal.
You must be aware of the diagnosis in the development inpatient and fever respiratory symptoms. Signs of respiratory failure investigation has been newly developed, the purulent secretion, increases when you find infiltrated the chest X-ray, the probability of leukocytosis. It was sent to the microbiology department for culture if there is a suspicion of pneumonia material from tracheal aspirate or sputum. It is done to explore the pleural if thoracentesis pleural effusion. (BAL) suggest that some of the risk for a known clinical diagnosis bronchoscopy for ventilator-associated pneumonia is suspected. Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) is a sub-type of hospital-acquired pneumonia that occur to people in the mechanical ventilation of (HAP). The name that is not characterized by causing VAP shown, but rather, during hospitalization, the definition of VAP has been limited to patients undergoing artificial respiration. Is an index of the fan associated with pneumonia, positive cultures after intubation to diagnose as such. Mechanism or cause to be classified according to it, it is recommended that you give the culture before the start of mechanical ventilation in order to compare in general.
In addition to streptococcal pharyngitis (angina), Streptococcus, certain types of necrotizing fasciitis pink eye, meningitis, bacterial pneumonia, endocarditis, and erysipelas (“carnivore I am responsible for many cases of “bacterial infection). However, Streptococcus many species are pathogenic, mouth, skin, intestine, and is part of the parasite microbiome of the human upper respiratory tract. In addition, Streptococcus is a necessary component in the production of Emmental (“Swiss”) cheese. Species of streptococci, are classified according to their hemolytic property. α hemolytic species gives the color greenish to blood agar medium in it, causing the oxidation of iron in the hemoglobin molecule in red blood cells. Of complete destruction of red blood cells β hemolysis type. The blood agar medium, it looks like a large area clear of blood cells around the bacterial colonies. γ hemolytic species, does not cause hemolysis. The β-hemolytic streptococcus, characterized by serotype from the description Lancefield carbohydrate specific present in the bacterial cell wall. Have not been described (except for J and I) Lancefield Group 20 serotypes known to V. In the medical environment, green chain groups and Streptococcus pneumoniae, B and β-hemolytic streptococcus Lancefield group also (, “A streptococci”, the most important group, “B and is α-hemolytic streptococcus S. It is known as streptococci “).