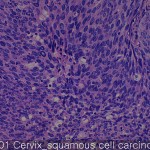
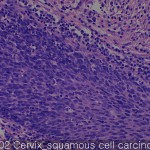
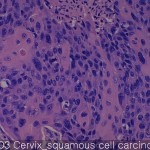
| Product name | Uterine cervix cancer-metastasis-normal |
| Cat. No. | CZA |
| Current version | CZA2 |
| Data sheet | CZA2.pdf |
| No. of samples | 50 |
| No. of patients | 59 |
| Core diameter | 2.0 mm |
| Section thickness | 4 micrometer |
| Price | 244 EUR |
| 320 USD | |
| 210 GBP | |
| Description | carcinoma: 50 cores metastatic cancer: 5 cores normal: 4 cores |
Product Related Literature
Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor derived from the cells of the cervix from. One of the most common symptoms of cervical cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding, but until the progression to advanced stages of cancer, there may be no obvious symptoms in some cases. Usually, is composed of (including local excision) surgery at an early stage, treatment is radiation therapy in advanced-stage disease and / or chemotherapy. Cancer screening using the Pap test can be used to identify pre-cancerous changes and potentially cancer cells and tissues of the cervix. Treatment of many changes, can prevent the development of cancer in many victims. In developed countries, the prevalence of screening programs for cervical cancer has decreased the incidence of invasive cervical cancer dramatically. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection seems to be factors necessary to the development of (90% +) in almost all cases of cervical cancer. HPV vaccine effective against the two strains of this large family of viruses responsible for about 70% of cases of cervical cancer currently are tested by United States, Canada, Australia and EU. Because it covers some vaccines cause cancer HPV only (“high risk”) type, after vaccination, you should seek medical screening smear regular even a woman.
It of the cervix is the narrow portion of the uterus join the top of the vagina. Cervical most cancers is an epithelial cell squamous cell carcinoma occurring in squamous (flat) line neck. Adenocarcinoma that occurs in glandular epithelial cells are the most common type of second. Very often, the cancer can occur in other types of cells of the cervix. It may be asymptomatic completely in the early stages of cervical cancer. Vaginal bleeding, vaginal mass (rarely) may indicate the presence of a malignant tumor or bleeding contact. In addition, moderate pain in between the symptoms vaginal discharge and intercourse, of cervical cancer. In advanced disease, metastases may be other places abdomen, lungs.
Symptoms of cervical cancer advanced included: pain loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, pelvic pain, back, foot pain, swelling of the legs, vaginal bleeding, fracture, and / or (rarely) vagina leakage of feces and urine from.
Infection of certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) is a risk factor of maximum for cervical cancer followed by smoking. The other risk factors, human immunodeficiency virus is included. Cause of cervical cancer not all are known, several factors involving other contributions. 18,31 and 45, which accounts for 70% of cervical cancer and 16 type [9] human papilloma virus, around the world, while the basis of another 10%.
Genital warts in the form of a benign tumor of epithelial cells was also caused by different strains of HPV. However, it is associated with cervical cancer serotypes thereof. It may include anything that may cause warts and these causes, cervical cancer, and a strain at the same time has been found. Been approved by other organizations and the American Cancer Society officially, HPV to develop cervical cancer, and is seen as, of conflict of formula (many, paradigm, infected patients as a result venereal disease receiving medically from cancer is a sexually transmitted disease but rather, this is) is caused technically is that you must have, but most women infected with high-risk HPV, and of developing cervical cancer. Condom is small, but it does not prevent the transmission always. Similarly, HPV can be transmitted by skin-to-skin contact with the infected area. Is considered the HPV and cleaning penis in the region, to grow preferentially in the epithelium of the glans can be prevention, but in men, the test commercially available for HPV, is not it.
Also smoking, can increase the risk of cervical cancer in women may be a method of directly and indirectly to induce cervical cancer of different cervical cancer.There some smoking associated with the development of the method. Direct way of agreement, have a great chance of occurrence in CIN3 that has the potential to start cervical cancer female smokers of this cancer. In the case of CIN3 lesions lead to cancer, I use a virus HPV most of them, but it can be considered that this is not necessarily so, directly, to be related to cervical cancer. Indirect method of developing this type of cancer from smoking is that can lead to cervical cancer leads to human papilloma virus. Long-term smokers appears to have risk of having CIN3 lesions lightly smoking or no smoking is low and heavy smoking. Smoking has been associated with cervical cancer, to help in the development of HPV is the main cause of this type of cancer. Further, not only promote the development of the HPV, if the woman is HPV positive already, the probability of infection of cervical cancer still increases it.
In many cases, the precursor potential cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to cervical cancer, are diagnosed in the study cervical biopsy by a pathologist. Classification was used for (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia) dysplastic change of pre-cancerous state of CIN.
Histological classification and naming of cervical cancer lesions percursor has been changed many times during the 20th century. Mild them, naming (CIS) cancer and dysplasia of moderate or severe, classification system of the World Health Organization, was the description of the lesion on the spot. Long-term cervical intraepithelial tumor (CIN), to focus on the spectrum of an abnormality in these lesions, was developed to standardize the therapy. Moderate dysplasia as CIN1, CIN2, and classifies the mild dysplasia, such as CIS and severe dysplasia as CIN3 it. In recent years, it will be combined with CIN2, CIN3, in CIN2 / 3 further. These results are what may be pathologist Report biopsy. They should not be confused with terms Bethesda system to achieve the results of the Pap (cytopathology). In the resulting of Bethesda: high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and (LSIL) low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL). Smear LSIL can be that corresponding to the CIN3 and CIN2 is to correspond to HSIL and CIN1, but you do not have to meet the histological findings, they are the result of Pap smear results and various tests.