| Product name | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor |
| Cat. No. | DAA |
| Current version | DAA2 |
| Data sheet | DAA2.pdf |
| No. of samples | 59 |
| No. of patients | 40 |
| Core diameter | 2.0 mm |
| Section thickness | 4 micrometer |
| Price | 244 EUR |
| 320 USD | |
| 210 GBP | |
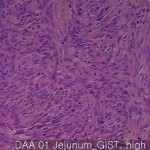
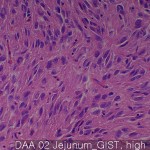
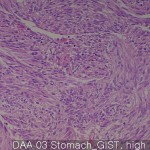
| Description | Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: 40 cores Metastatic or recurrent: 10 cores Normal smooth muscle: 9 cores |
Product Related Literature
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors are mesenchymal tumors most common in the digestive tract, which represents 1-3% of gastrointestinal tumors. They are due to mutations in the PDGFRA gene or gene action kit that generally, it is defined as a good or a tumor without positive staining kit.
GIST was introduced as a diagnostic term in 1983. At the end of the 1990s, it is referred to as a “tumor stromal gastrointestinal tract” non-epithelial tumors of many of the gastrointestinal tract. Histopathologists did not particularly be used to distinguish the species to know that now different molecules. Thereafter, it was identified as a marker which can distinguish between different types and subsequent CD34, CD117,. Furthermore, in the absence of a particular treatment, diagnostic classification has a limited impact therapeutic and prognostic.
Understanding of GIST of biology is remarkable, especially in-KIT, please change the identification of the molecular basis of GIST. Says 70-80% of GIST of, shortly thereafter be a benign and reviews, historical, literary before the molecular definition of GIST. Determination of the molecular basis for the result, of GIST in the exclusion of many tumors that contained a much greater number of tumors that have been labeled with different types of undifferentiated carcinoma and sarcoma, and also evaluated as early GIST-. For example, the diagnosis of some of the earlier of (malignant tumor of smooth muscle) leiomyosarcoma of the stomach or small intestine, then it is re-classified as GIST based on immunohistochemical staining. “Therefore. Benign” is considered GIST tumors of all and has been able GIST tumors and grade is classified as critical, GIST of all cancer staging of AJCC (7th Edition) / UICC you are eligible for classification. However, risk assessment of different tendency GIST by other recurrence or metastasis is dependent on the location of the origin of the number of mitotic figures, and size. Clinical pathway of care before 2000, was the value of information for the most part of the current era.
In other words, the sarcoma is a tumor of connective tissue, GISTs are non-epithelial Unlike the digestive tract tumor most. About 70%, occur in less than 10% of the esophagus and 20%, in the small intestine in the stomach. The degree of cell division is slow in the peritoneal cavity the liver, omentum and but if it is a large tumor dissemination, especially small tumor is benign in general. They are not found in other abdominal organs rarely. The GIST, are thought to have derived intermediate cells of Cajal, which is part of the autonomic nervous system of the intestine from (ICC) usually. They serve to control the functions of the pacemaker of the exercise.
GIST of about 85%, are associated with abnormal kit. -Kit growth factors known as (SCF) stem cell factor, is a gene encoding a transmembrane receptors. A small subset of c-Kit of, most (85%) resulting from mutations in the gene itself, and is associated with constitutive activation of KIT, which is detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent blotting kit specific time, the GIST of the association. And other cells product/CD117, represented by the number of some other bone marrow cells, mast cells, melanocytes, in particular ICC is C-kit. In the intestine, however, could be a GIST arising from the cells of MHC is high CD117 positive staining mass.
C-kit molecule contains a long extracellular domain, the intracellular portion and the transmembrane segment. Mutation found in DNA encoding (exon 11) intracellular portion which acts as an activator of tyrosine kinases other enzymes in general. Lead to genomic instability and possibly high rate of cell division, mutation, independent kitfunction made of activation by SCF. In cells with C-KIT mutations to development as GIST probably further mutations are “necessary,” but,-kitmutation is the first step of this process probably. Mutations in exon 11, 9, and Kit gene is important in drug therapy for GIST from 13-17 Metropolitan infrequent in GIST.The tyrosine kinase function of c-Kit, as will be described later. The 17 D816V mutant a-kit exon, is responsible for resistance to the targeted drug imatinib mesylate treatment such as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Wild-type having a mutation in the tyrosine kinase gene another, PDGFR-α (platelet-derived growth factor receptor α), associated in place (ie, unmutated), and kits, GIST cells most. Mutations of c-kit andPDGFrA of are mutually exclusive.
Small number of GIST, it appears NOR-kit, PDGFR-α also linked abnormally. GIST of the, occurs in 10 to 20 parts per million. Because of the diagnosis of GIST much sensitive a new way to the lab, there is a possibility that the higher the frequency of true. Expected frequency of GIST in the United States is about 5000 cases per year. In addition to making the most common form of GIST sarcoma not more than 70 kinds of cancer, which is less than 1% of all cancers in all its forms.